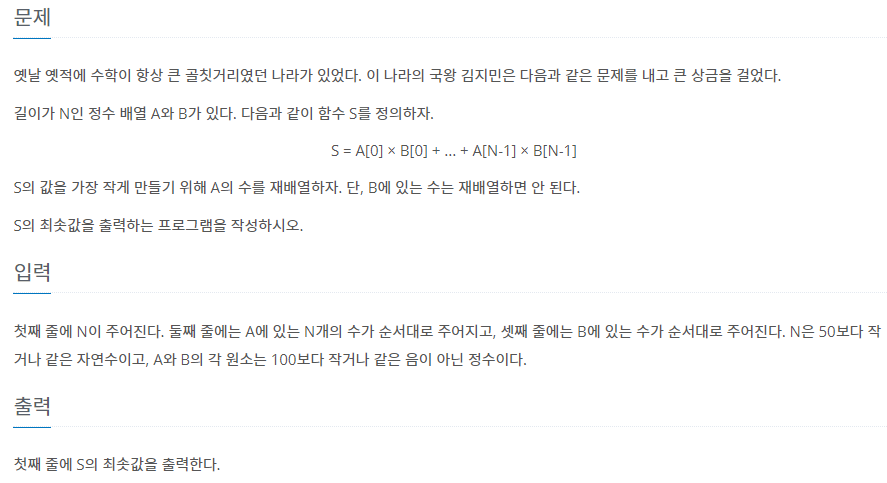
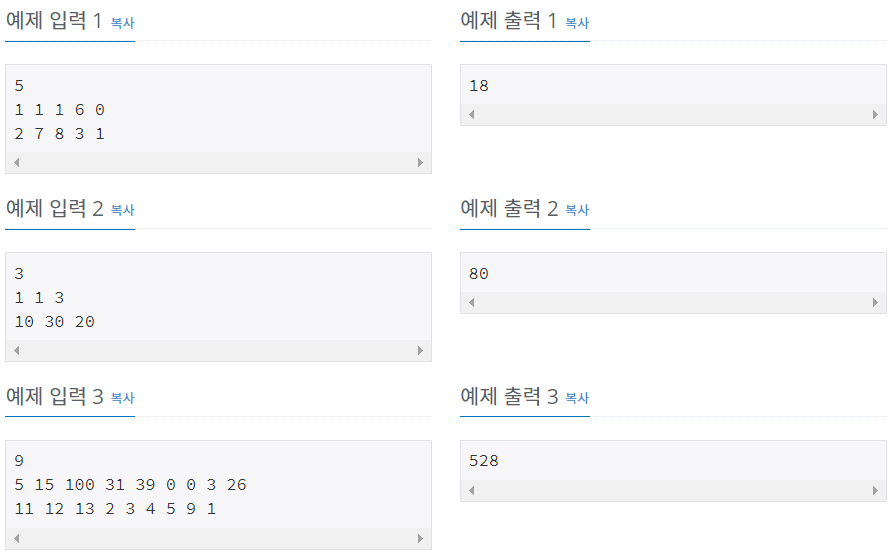
문제 이해하기
사실 B를 정렬하지말라고했지만 결과값만 판단하기때문에 B를 정렬해도 상관없긴하다..
하지만 B는 그대로 놔두고 풀어보기로했다!
최소값을 출력해야한다. = 가장큰수와 가장작은수를 곱하게하면된다.
A [1, 1, 1, 6, 0]
B [2, 7, 8, 3, 1]
tempB [2, 7, 8, 3, 1] : B를 그대로 복사한 배열
sortA [0, 1, 1, 1, 6] : A를 오름차순한 배열
sortB [8, 7, 3, 2, 1] : B를 내림차순한 배열
for (int i = 0; i < sortB.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < tempB.length; j++) {
if(sortB[i] == tempB[j]){
A[j] = sortA[i];
}
}
}위에처럼 B의 큰수부터 A의 작은수를 대입하면 풀릴 줄 알았는데... 오답처리되었다.
코드 자체에는 문제가없는데.. B 배열에 중복값이 있는 테스트케이스를 하나 더 생각해봤다.
A [1, 1, 1, 6, 0, 2]
B [2, 7, 3, 7, 3, 1]
sortA [0, 1, 1, 1, 2, 6]
sortB [7, 7, 3, 3, 2, 1]
tempB [2, 7, 3, 7, 3, 1]
for (int i = 0; i < sortB.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < tempB.length; j++) {
if(sortB[i] == tempB[j]){
System.out.print(j+", ");
A[j] = sortA[i];
}
}
}//j = 1, 3, 1, 3, 2, 4, 2, 4, 0, 5,
// A [2, 1, 1, 1, 1, 6]
//sortA [0, 1, 1, 1, 2, 6]
//sortB [7, 7, 3, 3, 2, 1]
//tempB [2, 7, 3, 7, 3, 1]
sortB[0](=7) == tempB[1](=7) 일때 A[1] = sortA[0](=0)
sortB[0](=7) == tempB[3](=7) 일때 A[3] = sortA[0](=0)
sortB[1](=7) == tempB[1](=7) 일때 A[1] = sortA[1](=1)
sortB[1](=7) == tempB[3](=7) 일때 A[3] = sortA[1](=1)
중복으로 값이 대입되는 경우가 발생되었다!!
sortB == tempB 실행은 1번만 일어나게하고, 한번 비교한 값은 -1로 변경하여 중복을 막았다
코드
import java.io.*;
import java.lang.reflect.Array;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
class Treasure {
int N;
int[] A;
int[] B;
void scan_input(String inputed) {
InputStream in = new ByteArrayInputStream(inputed.getBytes());
System.setIn(in);
}
void scan() throws IOException{
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringTokenizer st;
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
N = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
A = new int[N];
B = new int[N];
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) { A[i] = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()); }
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) { B[i] = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()); }
}
void process() {
Integer[] sortA = new Integer[N];
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) { sortA[i] = A[i]; }
Integer[] sortB = new Integer[N];
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) { sortB[i] = B[i]; }
Integer[] tempB = new Integer[N];
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) { tempB[i] = B[i]; }
//tempA는 오름차순 tempB의 내림차순
Arrays.sort(sortA);
Arrays.sort(sortB, Collections.reverseOrder());
for (int i = 0; i < sortB.length; i++) {
int overlap=0; //중복제거변수
for (int j = 0; j < tempB.length; j++) {
if(sortB[i] == tempB[j] && overlap == 0){
overlap++; //중복된 값은 1번만 나올 수 있도록
A[j] = sortA[i];
tempB[j] = -1; //아예 값을 변경해서 중복값을 제거
// System.out.println(sortA[i]);
// System.out.println("tempB "+Arrays.toString(tempB));
}
}
}
// System.out.println("A "+Arrays.toString(A));
// System.out.println("B "+Arrays.toString(B));
int result = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
result = result + (A[i] * B[i]);
}
System.out.println(result);
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Treasure r = new Treasure();
try {
r.scan();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
r.process();
}
}import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import java.io.IOException;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.*;
class MainTest {
@Test
void Test1(){
Treasure t = new Treasure();
t.scan_input("5\n" +
"1 1 1 6 0\n" +
"2 7 8 3 1");
try {
t.scan();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
t.process();
}
@Test
void Test2(){
Treasure t = new Treasure();
t.scan_input("3\n" +
"1 1 3\n" +
"10 30 20");
try {
t.scan();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
t.process();
}
@Test
void Test3(){
Treasure t = new Treasure();
t.scan_input("9\n" +
"5 15 100 31 39 0 0 3 26\n" +
"11 12 13 2 3 4 5 9 1");
try {
t.scan();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
t.process();
}
@Test
void Test4(){
Treasure t = new Treasure();
t.scan_input("6\n" +
"1 1 1 6 0 2\n" +
"2 7 3 7 3 1");
try {
t.scan();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
t.process();
}
}
성공!
'Coding Test' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [SWEA] 1206. [S/W 문제해결 기본] 1일차 - View (0) | 2022.02.10 |
|---|---|
| SWEA 1204. [S/W 문제해결 기본] 1일차 - 최빈수 구하기 (0) | 2022.02.10 |
| 백준 1946번 : 신입사원 (0) | 2021.10.26 |
| 백준 2217번 : 로프 (시간초과 해결과정) (0) | 2021.10.25 |
| 백준 2839번 : 설탕 배달 (2) | 2021.10.23 |
